Mixing And Blending, Powder Flow, Food Texture, Bulk Mixing, and Food Processing news and information
Mixing And Blending, Powder Flow, Food Texture, Bulk Mixing, and Food Processing news and information
PRODUCTS
-
Quick-Test adapters offer quick connect/disconnect with optional thread-on accuracy and self-alignment. They are available with 3.5mm and 2.4mm connectors up to 50 GHz.
-
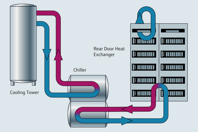
Energy costs are a major concern in data center cooling systems, with cooling accounting for up to 40% of total energy consumption. Efficient temperature measurement and control are crucial to minimizing these costs and ensuring the smooth operation of servers and equipment. Accurate temperature data helps prevent overheating, optimize cooling systems, and reduce energy usage, thereby maintaining equipment reliability and lowering operational costs.
-
The semi-automated capsule filler is part of the Explore Range, offering the potential to simplify formulation by eliminating the need for additional ‘formulation for powder filling’ steps.
-
When applied to plant influents, hydrogen peroxide destroys dissolved and/or total sulfide that otherwise scavenges Fe3+ added for CEPT and/or chemical phosphorus removal from wastewater. The foundational aspect of this PRI-TECH application (called PRI-CEPT) is that one lb of total sulfide theoretically consumes 3.5 lbs Fe3+ and thus represents an additional cost of $2 – 3 per lb influent sulfide.
-
Connect the right people to the right data at the right time with Trimble Connect, a cloud-based common data environment (CDE) and collaboration platform designed specifically for the construction industry.
WHITE PAPERS AND CASE STUDIES
-
AqueoUS Vets Named A Manufacturing Partner For A Southern CA Water Treatment Facility
In August 2018, Aqueous Vets was selected over existing industry incumbents to supply the Granular Activated Carbon Systems (GACS) for a Southern California Water Treatment Plant.
-
Re-Engineering A Complex Process For FDA Compliance
Discover the strategies that helped a company navigate a complex and shifting regulatory landscape to rapidly re-engineer a COVID-19 vaccine manufacturing process for FDA compliance.
-
How We Used Intelligent Automation to Transform Vendor Selection
Discover how your small biotech can achieve faster timelines, improved cost control, and more strategic, transparent choices with a platform leveraging intelligent automation.
-
Cell Line Development For High-Titer Lentivirus Vector Production
Explore a groundbreaking method to significantly enhance LV vector yield using engineered HEK293T cells. This approach paves the way for more efficient and large-scale production of LV vectors.
-
Achieving Excellence In Clinical Research And Quality Management
Lotus Clinical Research, founded in 2001, leverages regulatory expertise and digitalization to enhance quality, automate processes, and improve compliance in biopharmaceutical clinical trials.
-
Accelerating Early Phase Oncology Study Development
Explore a close collaboration to co-develop a comprehensive, adaptive protocol designed to support key decisions across multiple trial phases for an innovative cancer therapy.
-
Innovative Measurement Technology Enables Next Level Industrial AM
Reichenbacher Hamuel uses Ophir’s BeamPeek system to enhance laser quality in additive manufacturing, ensuring optimal beam performance and reliability across development, maintenance, and troubleshooting stages.
-
EHR-To-EDC Success In A Complex, Adaptive Platform Trial
I-SPY 2, one of the longest-running adaptive platform trials in oncology, is revolutionizing breast cancer research through a dynamic, data-driven approach to evaluating novel therapies.
-
Automated Trial Monitoring Workflows Make A Lean Team More Efficient
A pharmaceutical therapy developer was looking to automate reports, confirmation letters, and follow-up letters. See what happened when they adopted a cloud-based solution for end-to-end trial management.
-
Whether Half-Empty Or Half Full, Krohne Helps Back River Accurately Measure Flow
If a pipe in a wastewater treatment plant is only 50% filled, it doesn't matter whether you call a glass half full or half empty. When it comes to measuring the liquid in that pipe, either way presents a significant problem.
-
AMERICAN And Partners Install Boltless Restrained Underwater Pipeline System In Ashland, Wisconsin
Beneath the waters of Chequamegon Bay on Lake Superior in Ashland, Wisconsin, about 4,500 feet of 24-inch AMERICAN Flex-Ring Ductile Iron Pipe and a submerged timber crib intake structure were installed to ensure the city’s residents have quality drinking water for the next 100 years. The Ashland Water Intake Project began May 1, 2025, and is now complete.
-
Supporting Participants Through National Travel Disruptions
A sudden travel shutdown threatened a critical clinical visit. Rapid rescheduling, coordinated logistics, and clear communication ensured engagement and the ability to continue without interruption.
NEWS
-
How Lakes Connect To Groundwater Critical For Resilience To Climate Change7/9/2025
The study drew on data from 350 lakes across 18 European countries, collected between 2022 and 2024, to provide a comprehensive picture of how the continent’s lakes are coping with climate change.
-
Meatable And TruMeat Collaborate To Accelerate Cost-Effective Cultivated Meat Production4/30/2025
Meatable, the leader in cultivated meat technology, and TruMeat, specializing in the contract manufacturing of cultivated meat at commercial scale, have formed a strategic collaboration to advance the global commercialization of cultivated meat.
-
Baden-Württemberg's Largest Solar Park Now In Operation5/28/2025
EnBW has commissioned its solar park in Langenenslingen-Wilflingen (district of Biberach in the southwest of Germany).
-
Dielectric Partners With Foccus Digital For Brazilian Broadcast Growth8/15/2025
Dielectric’s Brazilian presence is about to radiate stronger through a new partnership with Foccus Digital that expand Dielectric’s broadcast business throughout the country.
-
Consulta Remedios Selects Kevel's Retail Media Cloud To Power Its Next-Generation Advertising Platform5/2/2025
Kevel, the leading provider of API-based retail media ad serving technology, today announced that Consulta Remédios, Brazil's largest medicine price comparison platform, has selected Kevel's Retail Media Cloud to power the development and enhancement of its in-house retail media network.
ABOUT
Mixing and Blending
Mixing and blending are terms that have specific meaning in the food industry. Most food processing experts use the word mixing to describe the process of combining wet and dry materials.
Blending is the term used to describe the process of combining only dry ingredients. The term blending is generally reserved for powders, flakes and granules of varying bulk densities and particle size that require gently blending and minimal contact with blender blades.
Agitation is often used synonymously with the term mixing. However, in food processing, agitation is used to ensure the mixing process to get a homogenous mix is completed faster.
Many industries require the mixing of free-flowing powders. The art of mixing involves different dilution geometries (a geometry is a way of combining unequal amounts of fine powders to ensure an equal distribution).
The geometric mix used depends on the size distribution, shape, particle density, composition and internal structures. Other properties include flow ability, bulk density, mixture quality, dustiness and properties of segregation.
Industrial mixers are used to do the blending and mixing. The shape and hardness of the materials being mixed affects the horsepower required to run the mixer. The type of mixer used in a production line varies depending on the materials that need to be mixed or blended. Paddle mixers are often the best choice for production line mixing because they are easy to clean, have less surface area, and have a minimal number of parts.
Mixing and blending is generally a sub-process within an overall process cycle so when placing a mixer it is important to consider how it integrates into the whole system. That includes impacts to both upstream and downstream product handling.